ARCHEOGRAPHUM, Qasr Amra Castle
Among the many historic castles in the Jordanian oriental desert, Qasr Amra is undoubtedly one of the most important. It is the only one listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, thanks to its exceptional conservation and the original frescoes that the monument harbors inside. These artistic series are indeed a rare testimony of the origins of Islamic art, being so far the only case so well-preserved with such ancient dating.
ARCHEOGRAPHUM was born as a tool for research, documentation and conservation of the heritage of this ancient Castle, which dates back to the eighth century. It collects data and bears witness to the restoration project conducted by ISCR in collaboration with the Department of Antiquities of the Kingdom of Jordan (DOA) and the World Monuments Fund (WMF), which began in 2011 and is currently underway. With ARCHEOGRAPHUM, it is possible to take a virtual tour of the Castle, thanks to the high-resolution images and 3D scans. We presented the project at the international conference “The Colours of the Prince.”
CLIENT MiBACT, ISCR di Roma, WMF, DOA
PARTNER Faro Technologies
YEAR 2012 – 2018
FEATURES
- HBIM Project
- Research, documentation and conservation Digital System
- Fieldwork offshoring
- Heritage digitalization
- Open and scalable project
- Virtual tour with 360 pictures
- Photogrammetry
- Laser scanner
- Content architecture
- Georeferenced data
- TAG System
- Open source graphic interface
- UX-UI
- Easily manageable backend
- Hierarchical user management
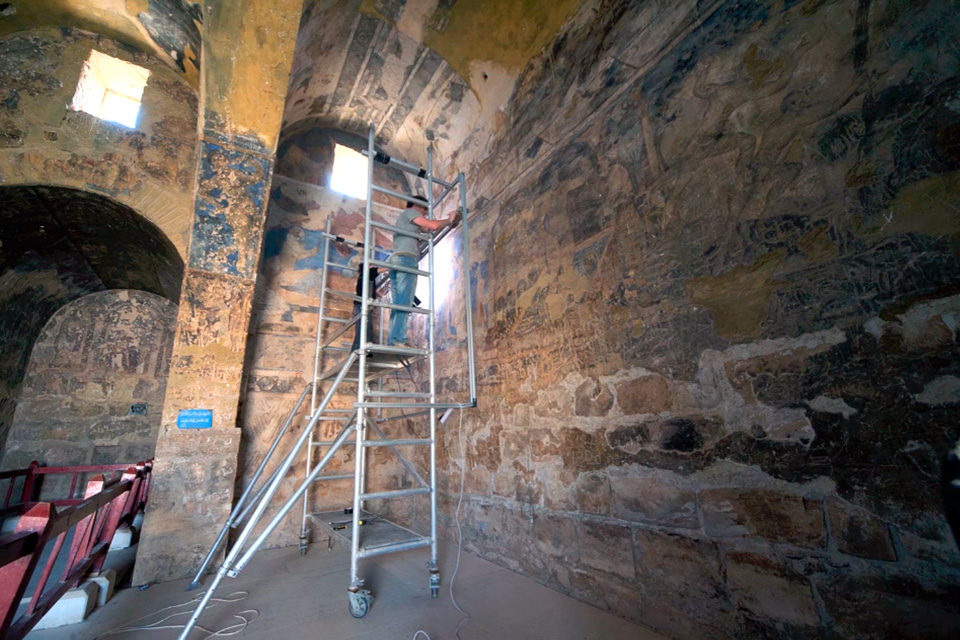

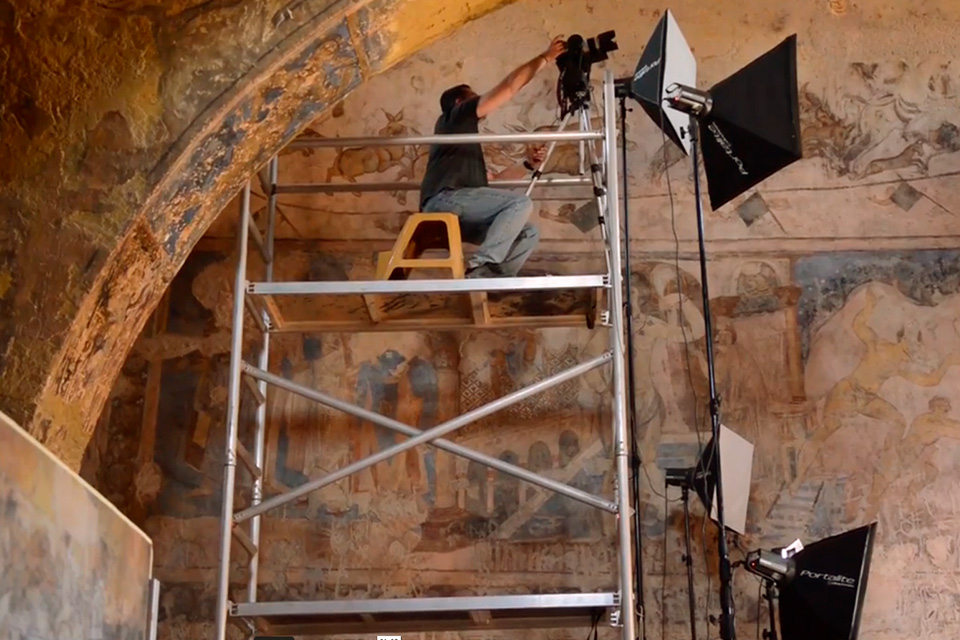
Project
Qasr Amra was built during the Umayyad Caliphate, which managed to unify a vast empire that spread from India to Spain. These desert castles were richly decorated with stuccoes, frescoes, mosaics, high reliefs and inlays. Qasr Amra’s famous wall paintings, for instance, cover an area of almost 380 square meters.
With the use of laser scanners and digital photogrammetry, we achieved a three-dimensional model of the rooms and decorations of the Castle, thus generating more than 5,000 high-resolution photographs and over 100 panoramic views.
ARCHEOGRAPHUM is a tool that stores and shares the documentation produced and archived according to the most advanced Building Information Modeling (BIM) systems, based on a participatory model and focused on data sharing.
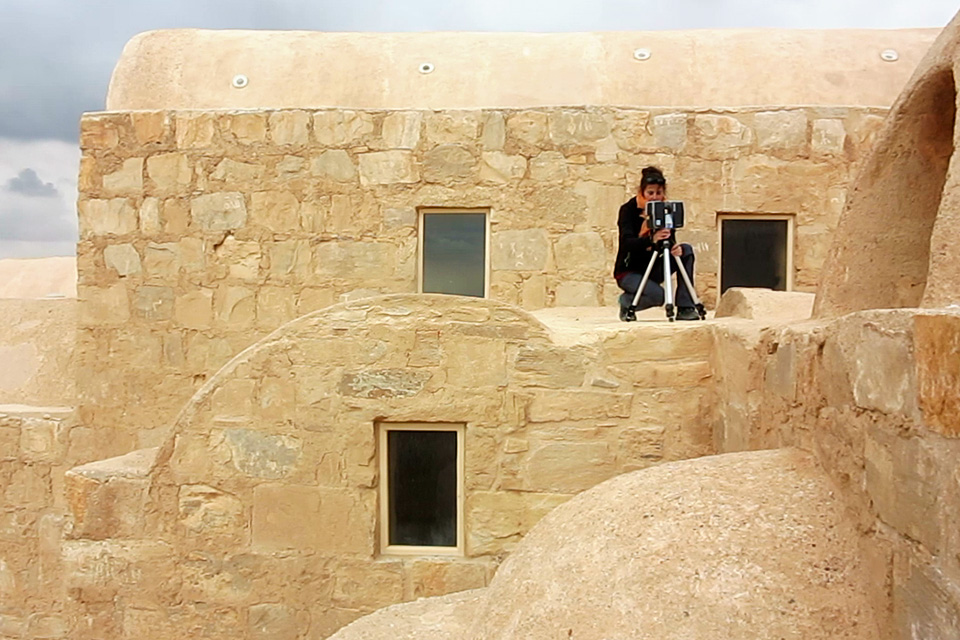
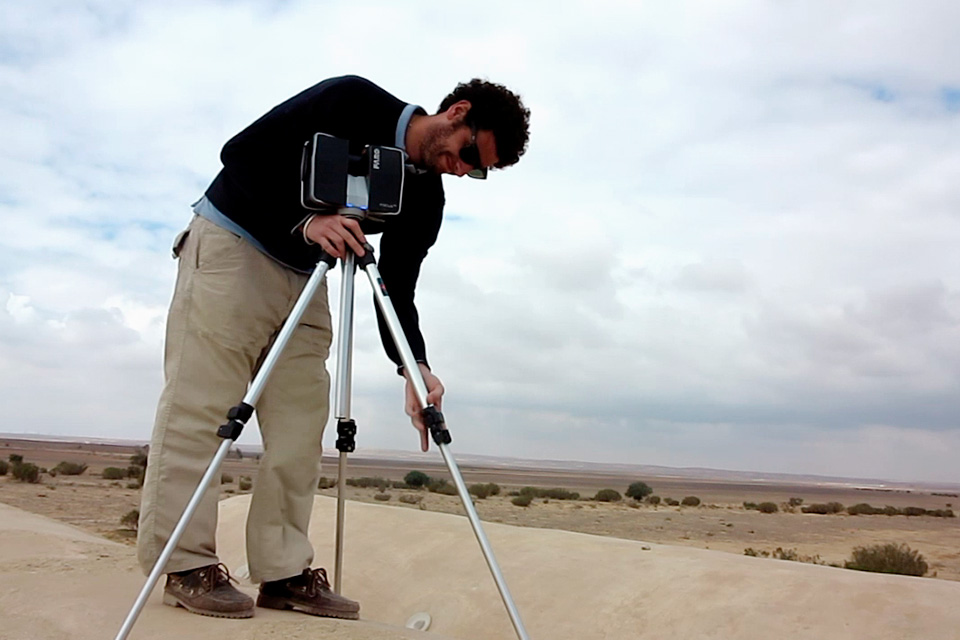


THREE-DIMENSIONAL SCANNING
To achieve an accurate and complete digital representation, we performed the 3D survey of the interiors and exteriors of Qasr Amra Castle by integrating different techniques.
Thanks to the laser scanner, which offers accurate three-dimension measurements of the surface of the space, we obtained topographic and architectural surveys in 3D of all the different parts of the monument.
Photogrammetry procures highly detailed pictures that are bigger than a 1:1 scale, with a level of magnification that the human eye could never perceive. With these macro photographs, we could bring back colors, tones, details and sharpness that otherwise could not be achieved.
Using specific software applied to the results, we accomplished a 3D model of the castle in its original shapes, sizes and colors, which also enabled the function of measuring distances between different points.
We could also verify the conditions of the structure and the restoration techniques that had been applied. In some cases, we could even restore the virtual stratigraphy of the pictorial decorations.
This project was developed in several stages by documenting step by step the work done by the restorers and the state of the castle before and after its restoration. The wall paintings had been covered with soot, dust and chemicals for decades, but the latest works revealed vibrant colors and yet unknown iconographic details, such as the Kufic Arabic inscription on the window on the south wall.

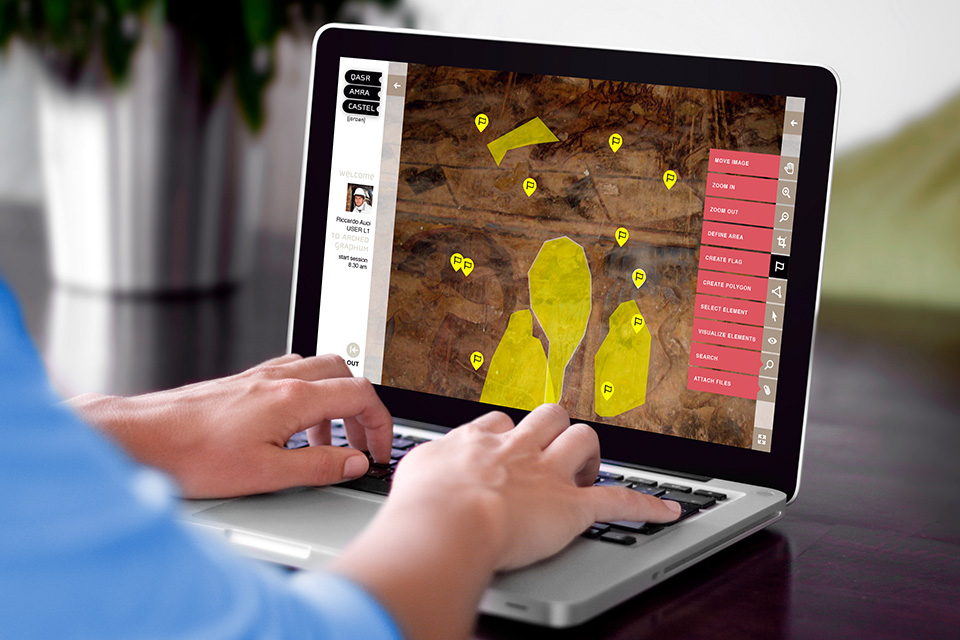
ARCHEOGRAPHUM
After digitalizing the heritage of Qasr Amra, we envisioned a tool that could manage the vast amount of data that we had gathered, where one could consult the updated material and, at the same time, add new information through the creation of new polygons. Also, we wanted to propose a useful instrument that allowed offshoring the fieldwork to work on it remotely.
ARCHEOGRAPHUM is a precise working tool for heritage research, documentation and protection based on new technologies, combining the scientific material of the monument’s database with the material obtained during the digitalization process.
All data and metadata are indexed and georeferenced, meaning that everything is linked to specific coordinates of the monument (through FLAGs) and associated with keywords (through TAGs) that help the search and information filtering. For this, we built ad hoc a specific lexicon and semantic structure relating all the contents loaded in the system.
Users are managed hierarchically with different access levels to the tools and information available. The graphic interface is simple and intuitive: once logged in, it unfolds the floorplan of the castle, where the user can select which area wants to consult or work.
There is a dropdown menu where the user can browse the frescoes and explore the monument virtually. The user also gets access to related information and can tag contents, attach files, or measure segments and polygons.
HBIM PROJECT
The project was selected by the HBIM (Smart Heritage Building Performance Measurement for Sustainability), which studies methods for the intelligent measurement of performance in historic buildings, such as the impact on their health and sustainability after reconstruction.
Working in BIM mode allows you to obtain a constantly updated overview of the progress of the work: thanks to the sharing of the single database, each variant developed by the work teams can be automatically shared by all the software tools.
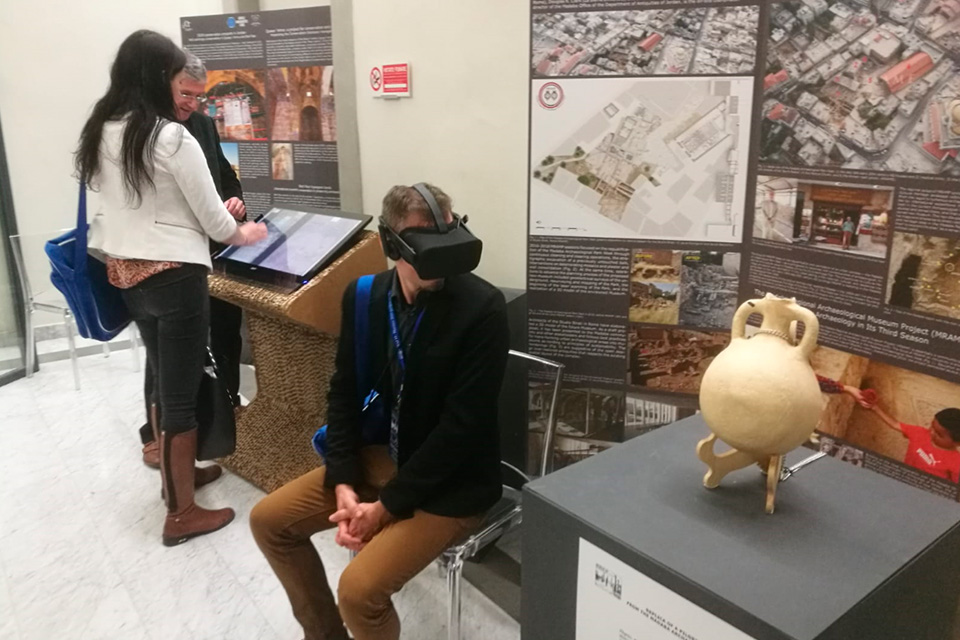
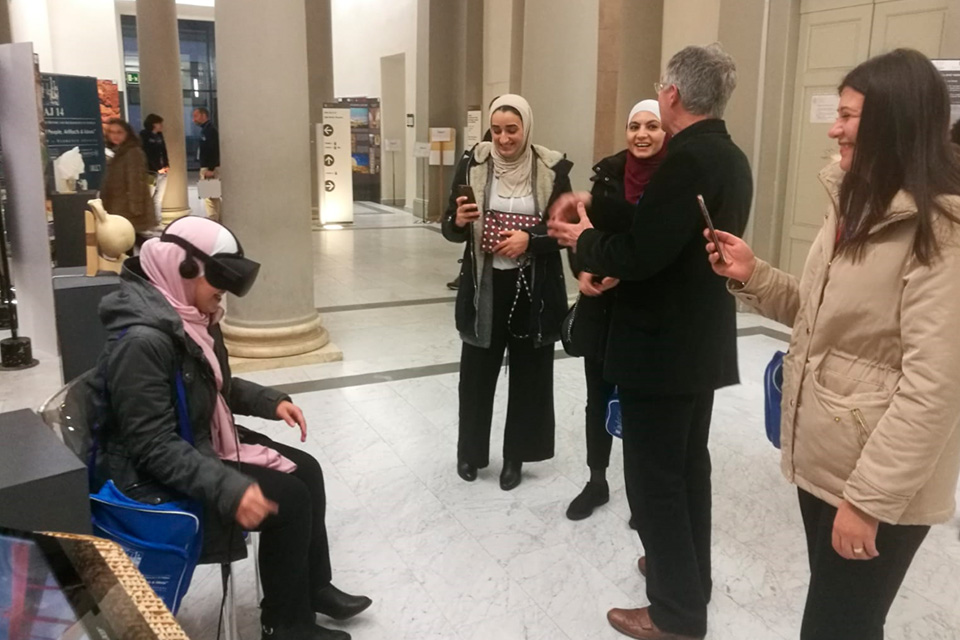



CONFERENCE “THE COLOURS OF THE PRINCE”
The project was presented at the conference “The Colours of the Prince” organized by MiBACT and the ISCR (Istituto Superiore per la Conservazione e il Restauro), held on October 22 and 23, 2014.
It was a precious opportunity for us to discuss with cultural agents and prominent international academics the whole project of restoration and conservation of Qasr Amra, and to talk about ARCHEOGRAPHUM and its applications.
VIDEO FOR THE WORLD MONUMENTS FUND
The World Monuments Fund commissioned us with the dissemination of ARCHEOGRAPHUM, for which we produced a presentation video featuring interviews with the project’s international reference figures. Among them were Gaetano Palumbo, who back then was director of projects at the WMF, Asma Shhaltoug, director of engineering and conservation at the DOA (Department of Antiquities of the Kingdom of Jordan), and Giovanna de Palma, an archaeologist at the ISCR in Rome.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS – ISCR of Rome
The ISCR of Rome students’ contribution was fundamental for the realization of the entire project. Their help was indispensable for creating ARCHEOGRAPHUM, for example, in the analysis and subdivision of the castle, or the research and analysis of the specific vocabulary.
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
PROGRAMMING
- Mysql
SOFTWARE
- Krpano
PRESS
Destellos de Color en el Desierto: La restauración de Qusair Amra
National Geographic
Il sito di Qusayr ‘Amra insignito del Best Practice Award ICCROM-ATHAR
Istituto Centrale per il Restauro
Qysayr ‘Amra: a World Heritage Site
World Monuments Fund